Other Names
Rabbit Coagulation Factor XII ELISA kit
F12; FXII; HAF; Contact Factor; Hageman Factor
Research Area
FXII; HAF; Contact Factor; Hageman Factor
Background
This gene encodes the coagulation factor XIII A subunit. Coagulation factor XIII is the last zymogen to become activated in the blood coagulation cascade. Plasma factor XIII is a heterotetramer composed of 2 A subunits and 2 B subunits. The A subunits have catalytic function, and the B subunits do not have enzymatic activity and may serve as plasma carrier molecules. Platelet factor XIII is comprised only of 2 A subunits, which are identical to those of plasma origin. Upon cleavage of the activation peptide by thrombin and in the presence of calcium ion, the plasma factor XIII dissociates its B subunits and yields the same active enzyme, factor XIIIa, as platelet factor XIII. This enzyme acts as a transglutaminase to catalyze the formation of gamma-glutamyl-epsilon-lysine crosslinking between fibrin molecules, thus stabilizing the fibrin clot. It also crosslinks alpha-2-plasmin inhibitor, or fibronectin, to the alpha chains of fibrin. Factor XIII deficiency is classified into two categories: type I deficiency, characterized by the lack of both the A and B subunits; and type II deficiency, characterized by the lack of the A subunit alone. These defects can result in a lifelong bleeding tendency, defective wound healing, and habitual abortion.
|
Product Name |
F12 ELISA |
|
Species |
Rabbit |
|
Product Size |
96/48 Tests |
|
Concentration |
0.5-10 ng/mL |
|
Sensitivity |
0.07 ng/mL |
|
Principle |
Competitive ELISA |
|
Sample Volume |
100 ul |
|
Assay Time |
90 minutes |
|
Platform |
Microplate Reader |
|
Conjugate |
HRP |
|
Detection Method |
Colorimetric |
|
Storage |
2-8°C |
|
|
For Research use only
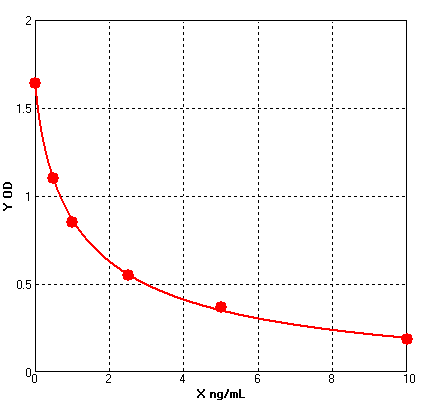
Four parameter Logisticcurve regression
Formular: y = (A - D) / [1 + (x/C)^B] + D
A = 1.64300 B = 0.80240 C = 1.28822 D = -0.08874 r^2 = 0.99950 |
1. Protocols for ELISA
![]() 1) Direct ELISA
1) Direct ELISA
![]() 2) Direct ELISA Using Fluorescent Substrate
2) Direct ELISA Using Fluorescent Substrate
![]() 3) Indirect ELISA
3) Indirect ELISA
![]() 4) Sandwich ELISA
4) Sandwich ELISA
2. Protocols for IHC ICC
![]() 1) Determining if the antibody binds only phosphorylated protein (WB or IHC)
1) Determining if the antibody binds only phosphorylated protein (WB or IHC)
![]() 2) Double immunofluorescence-sequential protocol
2) Double immunofluorescence-sequential protocol
![]() 3) Double immunofluorescence-simultaneous protocol
3) Double immunofluorescence-simultaneous protocol
![]() 4) Fixation and Permeabilization In IHC ICC
4) Fixation and Permeabilization In IHC ICC
![]() 5) Glycol Methalacrylate Acrylic Resin Embedding For IHC
5) Glycol Methalacrylate Acrylic Resin Embedding For IHC
![]() 9) Immunohistochemistry (IHC-Fr) - Frozen Sections
9) Immunohistochemistry (IHC-Fr) - Frozen Sections
3. Protocols for WB
![]() 4) S-100 Mitochondrial Fractionation
4) S-100 Mitochondrial Fractionation
![]() 5) Stripping for Reprobing Western Blots
5) Stripping for Reprobing Western Blots
![]() 7) Western Blotting - A Beginner's Guide
7) Western Blotting - A Beginner's Guide
![]() 8) Western Blotting of Phospho-Proteins
8) Western Blotting of Phospho-Proteins
![]() 9) Western Blotting Using Antibodies Against Histone Proteins
9) Western Blotting Using Antibodies Against Histone Proteins
4. Protocols for IP
![]() 2) Using IgM antibodies for IP
2) Using IgM antibodies for IP
5. Protocols for FACS
![]() 1) Direct Staining Protocol (Cell Surface Staining)
1) Direct Staining Protocol (Cell Surface Staining)
![]() 3) Flow Cytometry Whole Blood Samples-Red Blood Cell Lysis
3) Flow Cytometry Whole Blood Samples-Red Blood Cell Lysis
![]() 4) Indirect Staining Protocol (Cell Surface Staining)
4) Indirect Staining Protocol (Cell Surface Staining)
![]() 6) Recommended Controls for FACS
6) Recommended Controls for FACS
6. Protocols for ELISPOT
![]() 1) ELISPOT
1) ELISPOT
1. Protocols for ELISA
![]() 1) Direct ELISA
1) Direct ELISA
![]() 2) Direct ELISA Using Fluorescent Substrate
2) Direct ELISA Using Fluorescent Substrate
![]() 3) Indirect ELISA
3) Indirect ELISA
![]() 4) Sandwich ELISA
4) Sandwich ELISA
2. Protocols for IHC ICC
![]() 1) Determining if the antibody binds only phosphorylated protein (WB or IHC)
1) Determining if the antibody binds only phosphorylated protein (WB or IHC)
![]() 2) Double immunofluorescence-sequential protocol
2) Double immunofluorescence-sequential protocol
![]() 3) Double immunofluorescence-simultaneous protocol
3) Double immunofluorescence-simultaneous protocol
![]() 4) Fixation and Permeabilization In IHC ICC
4) Fixation and Permeabilization In IHC ICC
![]() 5) Glycol Methalacrylate Acrylic Resin Embedding For IHC
5) Glycol Methalacrylate Acrylic Resin Embedding For IHC
![]() 9) Immunohistochemistry (IHC-Fr) - Frozen Sections
9) Immunohistochemistry (IHC-Fr) - Frozen Sections
3. Protocols for WB
![]() 4) S-100 Mitochondrial Fractionation
4) S-100 Mitochondrial Fractionation
![]() 5) Stripping for Reprobing Western Blots
5) Stripping for Reprobing Western Blots
![]() 7) Western Blotting - A Beginner's Guide
7) Western Blotting - A Beginner's Guide
![]() 8) Western Blotting of Phospho-Proteins
8) Western Blotting of Phospho-Proteins
![]() 9) Western Blotting Using Antibodies Against Histone Proteins
9) Western Blotting Using Antibodies Against Histone Proteins
4. Protocols for IP
![]() 2) Using IgM antibodies for IP
2) Using IgM antibodies for IP
5. Protocols for FACS
![]() 1) Direct Staining Protocol (Cell Surface Staining)
1) Direct Staining Protocol (Cell Surface Staining)
![]() 3) Flow Cytometry Whole Blood Samples-Red Blood Cell Lysis
3) Flow Cytometry Whole Blood Samples-Red Blood Cell Lysis
![]() 4) Indirect Staining Protocol (Cell Surface Staining)
4) Indirect Staining Protocol (Cell Surface Staining)
![]() 6) Recommended Controls for FACS
6) Recommended Controls for FACS
6. Protocols for ELISPOT
![]() 1) ELISPOT
1) ELISPOT

 SDS
SDS