Other Names
ELN; WBS, WS, SVAS; Tropoelastin; Supravalvular Aortic Stenosis; Williams-Beuren Syndrome
Research Area
Cardiovascular, Signal Transduction
Background
Elastic fibers, which are comprised primarily of elastin, endow loose connective tissue with a resilience that compliments the tensile strength of collagenous fibers. Elastin is the main component of the extracellular matrix of arteries, and it performs a regulatory function during arterial development by controlling proliferation of smooth muscle and stabilizing arterial structure. Elastin is composed largely of glycine, proline, and other hydrophobic residues, and it contains multiple lysine-derived crosslinks, such as desmosines, which link individual polypeptide chains into a rubber-like network. During aging, the elasticity of connective tissue becomes reduced because of the cross-linking of collagenous fibers with elastin. Deficiencies of elastin are associated with multiple disorders, such as supravalvular aortic stenosis and Williams-Beuren syndrome. The human elastin gene maps to chromosome 7q11.23.
|
Product Name |
ELN ELISA |
|
Species |
Rat |
|
Product Size |
96/48 Tests |
|
Concentration |
25-500 ng/mL |
|
Sensitivity |
1.7 ng/mL |
|
Principle |
Competitive ELISA |
|
Sample Volume |
100 ul |
|
Assay Time |
90 minutes |
|
Platform |
Microplate Reader |
|
Conjugate |
HRP |
|
Detection Method |
Colorimetric |
|
Storage |
2-8°C |
|
|
For reference use only.
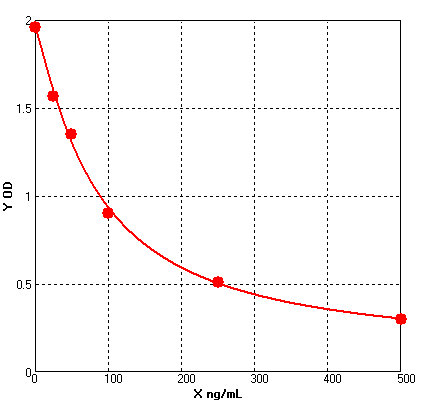
Four parameter Logisticcurve regression
Formular: y = (A - D) / [1 + (x/C)^B] + D
A = 1.95326
B = 1.17756
C = 84.40109
D = 0.09779
r^2 = 0.99797
|
1. Protocols for ELISA
![]() 1) Direct ELISA
1) Direct ELISA
![]() 2) Direct ELISA Using Fluorescent Substrate
2) Direct ELISA Using Fluorescent Substrate
![]() 3) Indirect ELISA
3) Indirect ELISA
![]() 4) Sandwich ELISA
4) Sandwich ELISA
2. Protocols for IHC ICC
![]() 1) Determining if the antibody binds only phosphorylated protein (WB or IHC)
1) Determining if the antibody binds only phosphorylated protein (WB or IHC)
![]() 2) Double immunofluorescence-sequential protocol
2) Double immunofluorescence-sequential protocol
![]() 3) Double immunofluorescence-simultaneous protocol
3) Double immunofluorescence-simultaneous protocol
![]() 4) Fixation and Permeabilization In IHC ICC
4) Fixation and Permeabilization In IHC ICC
![]() 5) Glycol Methalacrylate Acrylic Resin Embedding For IHC
5) Glycol Methalacrylate Acrylic Resin Embedding For IHC
![]() 9) Immunohistochemistry (IHC-Fr) - Frozen Sections
9) Immunohistochemistry (IHC-Fr) - Frozen Sections
3. Protocols for WB
![]() 4) S-100 Mitochondrial Fractionation
4) S-100 Mitochondrial Fractionation
![]() 5) Stripping for Reprobing Western Blots
5) Stripping for Reprobing Western Blots
![]() 7) Western Blotting - A Beginner's Guide
7) Western Blotting - A Beginner's Guide
![]() 8) Western Blotting of Phospho-Proteins
8) Western Blotting of Phospho-Proteins
![]() 9) Western Blotting Using Antibodies Against Histone Proteins
9) Western Blotting Using Antibodies Against Histone Proteins
4. Protocols for IP
![]() 2) Using IgM antibodies for IP
2) Using IgM antibodies for IP
5. Protocols for FACS
![]() 1) Direct Staining Protocol (Cell Surface Staining)
1) Direct Staining Protocol (Cell Surface Staining)
![]() 3) Flow Cytometry Whole Blood Samples-Red Blood Cell Lysis
3) Flow Cytometry Whole Blood Samples-Red Blood Cell Lysis
![]() 4) Indirect Staining Protocol (Cell Surface Staining)
4) Indirect Staining Protocol (Cell Surface Staining)
![]() 6) Recommended Controls for FACS
6) Recommended Controls for FACS
6. Protocols for ELISPOT
![]() 1) ELISPOT
1) ELISPOT
1. Do I have to run all of my standards and samples in duplicate?
Yes, the duplicates are run in order to monitor assay precision and increase confidence in the assay results obtained.
2. Do I have to run all of my samples at one time?
No, each kit uses stripwell microplate. This allows the user to analyse different numbers of samples at different times.
3. What types of reproducible results are obtained with the assays?
Each kit comes with a manual containing a graph of typical data obtained. Any variation in operator, pipetting and washing technique, incubation time or temperature, and kit age can cause variation in result. Each user should obtain their own standard curve.
4. Is it possible to store the reagents other than indicated?
Storage of the kit components under conditions other than indicated is not recommended in order to assure proper performance of the test.
5. How should I store my samples?
Samples should be stored at -20oC or lower temperature. For long-term storage, it is recommended to freeze them at -70oC -80oC.
6. Can I modify the protocol?
BG ELISA kits have been optimized to provide the best possible results. Modifying the format or protocol may give inaccurate and wrong results.
7. Can I use a sample type that is not recommended in the kit insert?
The kit has been validated for the sample types listed in the kit insert. Sample types other than those validated have not been tested. Contact Technical Service for further information.
8. My samples generated values that were outside the dynamic range of the assay. Can I use these values?
It is recommended that only sample values that fall within the range of the standard curve be used. Values outside the range of the standard curve are generally non-linear, which can lead to incorrectly extrapolated values. Samples that generate values higher than the highest standard should be (further) diluted and the assay repeated. If samples fall below the range of the assay, the sample is considered to be non-detectable.
9. Do I have to run a Blank or Zero Standards every time?
Yes, these are required for the calculations, and reflect any subtle but significant performance changes from day to day and assay to assay. They are also extremely helpful when troubleshooting the source of a particular assay problem.
10. Can I alter the volume of sample I use in the assay?
It is not recommended that you alter the volumes since all BG kits are designed for optimal performance at the given volumes
11. Can components from different kits be used?
Each kit contains components which have specific lot numbers to ensure that all of the components are performing optimally alone, as well as with all of the other components in the kit. QC testing is performed on these specific lots. It is never recommended to use your own components or components from other kits or vendors.
12. My standard curve looked fine, but I didn’t get a signal in my sample when I expected to, why?
The sample may not contain the analyte. A matrix effect may be masking the detection. Ensure that the recommended dilution was followed as stated in the kit insert. If dilution was recommended, check to be sure that the dilution was performed properly. Over-dilution may cause the sample to fall below the range of the standard curve.
13. How do you recommend I wash my plate?
If you are using an automated plate washer we recommend that the calibration be checked on a regular basis, and that the system is flushed with the Plate Washing Buffer prior to washing. The same is true for a manual washer. A repeater or a wash bottle can also be used. The user should be careful to ensure that all of the contents are aspirated and the plate tapped dry on lint-free paper.
14. Do I need to use a plate shaker?
Reliable results can be obtained without a plate shaker, but the O.D.'s will generally be lower than those obtained using a plate shaker.
15. Why do I have to use wavelength correction between 450-570nm?
For the ELISA assay, reading at dual wavelengths is done to correct for the optical density contributed by the plastic well, the lamp and optical fluctuations.
16. If I extract my sample, do I still need to follow the recommended dilutions given in the kit insert?
The amount of sample dilution needed after an extraction procedure will be affected by the effects of purification and concentration in the protocol used. The amount of dilution or concentration will have to be determined by the end-user.
17. What is the expected concentration of analyte that I should expect to find?
The amount of a given analyte may vary not only from species-to-species, but also between tissue and cellular sources. The best source of this information is the current literature that is easily accessed through the Internet at multiple scientific databases.
18. My optical densities were a little higher (or lower) than those in the manual that came with my kit. Why?
The optical density is affected by a number of physical conditions such as time and temperature. We suggest that you shorten or lengthen the final incubation with substrate solution to compensate.
19. What are the reasons for High Background?
1) Improper Washing: Check volume of washing buffer reservoir and make sure all recommended washing steps are performed.
2) Contaminated Substrate: Make sure there is no contamination of the substrate with metal ions or oxidizing reagents, before use. Keep the extra substrate solution separately during the ELISA substrate development time.
3) Substrate exposed to light: Exposure to light may result in a blue color of the substrate. Keep solutions in the dark (vial) until ready to dispense into the plate.
4) Wrong Incubation Times/Temperatures: Generally follow the test protocol regarding incubation times and temperatures. However, if all wells are intensely and equally colored with no intensity gradient observed in the standard dilution series, then it may be necessary to observe the substrate reaction as the color is developing, in order to stop the reaction sooner.

 SDS
SDS